Are you interested in learning what is SEO? This is not nuclear physics and it is very easy if you follow this entire guide thoroughly.
I created this article with everything that I have learned in my 4 years of SEO work in national and international projects. Are you staying to find out?
Hello folks, my name is Puneet Sharma and today I am going to explain to you everything that you need to know in order to learn everything about SEO.
What is SEO?
Unless you are a newcomer to this world, surely you know the definition of SEO or Search Engine Optimization well. However, I will tell you what SEO means:
SEO or search engine optimization is the art of making improvements both in the internal structure of the page (on-page) and in the external structure (off-page) to position our pages at the top of the search engines at the moment in which users perform searches.
Why is SEO important?
You’ve probably heard or read more than once that SEO is dead. Well, I do not believe that at all. Google can anticipate user intent and improve search results.
Currently, it is only possible to do SEO by working rigorously, professionally, and thinking of the user before the search engines. Do you still doubt the importance of SEO strategies? We give you some information:
We know that the top 10 search results account for almost 100% of visits (if you’re not on the first page, you don’t exist). Now, how are these clicks distributed?
- Top1: receives about 1/3rd of the clicks.
- Top2: you benefit from slightly less than 20% of the traffic.
- Top3: users who click on this result are around 10% of the total.
That is, for a keyword like “SEO agency” (about 6,000 monthly searches), you could aspire to:
- Top1: about 2,000 visits per month
- Top2: about 1,200 visits per month
- Top3: about 600 visits per month
Interesting, right?
How do Google and other search engines work?
As I have already mentioned, the priority of search engines is to offer the user exactly what they are looking for at the time they need it. To do this, they collect, index, and organize all the information available on the Internet and return it ordered according to its relevance when the Internet user makes a query.
Keywords vs. Search Intention
In SEO, we have traditionally identified that user queries with the keywords that we had to work on to the position for the pages that interested us. Today we know that it does not work exactly like that and we have replaced the old keywords with search intent, a much broader concept capable of better capturing the needs of a user.
We can define the search intention as the need for information that the user has at a specific time, while the keywords or keywords would be the exact written expression of that need that they enter in the search engine. Thus, we find that for the same search intention there can be an infinity of different keywords and on the contrary, a single keyword without context can respond to different intentions.
As SEOs, my job is to optimize our pages so that they respond in the best possible way to the search intention of my potential clients: only in this way will we be able to reach the top of the ranking.
Keywords vs. Search Intention
In SEO, we have traditionally identified that user queries with the keywords that we had to work on to the position for the pages that interested us. Today we know that it does not work exactly like that and we have replaced the old keywords with search intent, a much broader concept capable of better capturing the needs of a user.
We can define the search intention as the need for information that the user has at a specific time, while the keywords or keywords would be the exact written expression of that need that they enter in the search engine. Thus, we find that for the same search intention there can be an infinity of different keywords and on the contrary, a single keyword without context can respond to different intentions.
As SEOs, my job is to optimize our pages so that they respond in the best possible way to the search intention of my potential clients: only in this way will we be able to reach the top of the ranking.
Machine Learning, RankBrain, and BERT
But, how is the search engine able to interpret the search intention of a user? Over the last few years, algorithms have taken giant steps in the use of artificial intelligence that allowed machines to understand more and better human needs and the way they express them.
Although it still sounds like science fiction, machine learning is a technology that has been in our lives for years. In simple words, it is nothing more than the ability of a computer to extract patterns behind a set of examples and extrapolate them to different situations.
Applied to Google, and simplifying a lot, machine learning is capable of extracting similar patterns in queries and crossing them with the search results chosen by users, refining these more and more to offer more and more accurate answers.
We can consider RankBrain the natural evolution of machine learning systems since it is a self-learning system applied to user searches and based on artificial intelligence, which was a real revolution when it was made public in 2015.
The function of RankBrain is to interpret the words that users enter in the search engine and relate them to a specific search intention. To do this, it not only checks the documents in its database looking for the occurrence of said words but also applies semantics and is capable of learning from itself and resorting to that stored knowledge in the face of new complex or unknown queries, such as the use of neologisms.
Finally, BERT is Google’s latest great innovation in terms of artificial intelligence applied to search (and we say great innovation because it is known that the algorithm changes practically daily, introducing small modifications of which we are not always aware).
BERT is the acronym for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers and it is in this bidirectionality where the real novelty is found: BERT can analyze the words both to the right and to the left of the keyword, which gives it a greater understanding of the context and, therefore, of the user’s search.
Are you thinking about how to optimize your content for BERT? The question is wrong: according to Google itself, the right thing to do is create quality content focused on the user, forgetting the algorithm.
The Concept of Authority or EAT
Another of the positioning factors that Google takes into account when forming the results rankings is what is known as EAT. Which is nothing more than the acronym for Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness, that is, experience, authority, and trust.
Since the implementation of this algorithm, the search engine has taken much more into account who is the author of the content and what level of trust can be given to their words based on their experience and authority as an expert on the subject. This update has especially influenced medical, scientific websites, or all those that fall within the Your Money, Your Life segment, which we will see in the next point.
YMYL Sectors
Closely related to the EAT update, websites with YMYL content are all those from sectors in which erroneous, malicious, or low-quality content can negatively affect people’s lives, be it their health, their economy, or their happiness.
Some of the classic YMYL topics are finances, medical or health information, legal subjects (especially related to childhood, divorces, or wills), legislation and citizenship, etc.
SEO Penalties And Why avoid them?
As the poet said, “whoever suffered it knows it.” A penalty is a “punishment” that Google imposes on websites that do not comply with its anti-spam guidelines. There are different types of penalties, depending on the type of sanction imposed and according to its effect.
Types of penalty:
- Algorithmic – Automatically imposed by a Google algorithm update. Two of the most famous have been Panda, related to the quality of the content, and Penguin, which fought against spam in the links.
- Manual: imposed by one of Google’s employees who by spam, keyword stuffing (over-optimization of keywords), thin content (content without value), or unnatural link pattern (both from our website to the outside and from others to ours).
Effect of the sanction:
- Keyword: one or more positioned keywords lose positions in the ranking. It is more serious the more business core the punished keywords are.
- URL or directory: a massive drop of all the keywords that were ranking for that URL or directory.
- Subdomain: same as above, but for a complete subdomain.
- Domain: even more serious, it affects the keywords positioned throughout the domain.
- Exclusion from the index or delisting: the most serious of the penalties imposed. If Google decides to de-index an entire website, none of its content will appear in search results.
Recovering from an SEO penalty is not easy: first, you need to audit the web to find the error that caused the punishment (in some cases it is more evident than in others) and fix it. Even so, it can take months for the search engine to reverse the punishment and, even in very serious cases, it may be necessary to apply extreme measures, such as changing the domain for a “clean” one.
Local SEO: Towards Maximum Personalization in Search Results
As we have seen so far, all Google updates go in the same direction: improving the user experience, covering their search intent, and offering exactly what they are looking for when they need it. The local SEO is the ultimate expression of that customization.
With the generation of Internet use on mobile devices (smartphones and tablets), Google has understood that users can make inquiries from anywhere, and, many times, the results of these inquiries are intrinsically related to the place from which they are made.
A clear example of a local search is “vegan restaurant”. The search engine understands that the query is related to the search for a place to dine and offers us the closest results to us.
I am not going to explain here a complete local SEO strategy, which could be used for several posts, but if you want to succeed in the local SERPs, you must keep a few things in mind:
- Relevance: understood as the correspondence between the user’s search intention and the business product or service.
- Proximity: proximity of the business to the place from which the search is carried out.
- Prominence: the ratings of users through the review system, as well as the on-page and off-page factors of the web page, serve Google to evaluate the quality of the web page.
In addition, you can support your local strategy by correctly optimizing the My Business tab, which will help you appear on Google Maps when your customers search near you.
Ranking Factors for Google
Below, you will see 19 factors that are highly relevant when it comes to positioning your website. Within each point, you will find a bit of humble advice (based on experience) that seeks to help you apply each point to your website/business. In this way, you will not only discover a series of concepts but you can apply them directly. Let’s go there!
1. Types of Search Intent
We can classify the search intention into 3 large groups:
- Information searches (they try to find descriptive information in order to understand the concept. Example = first president of USA.)
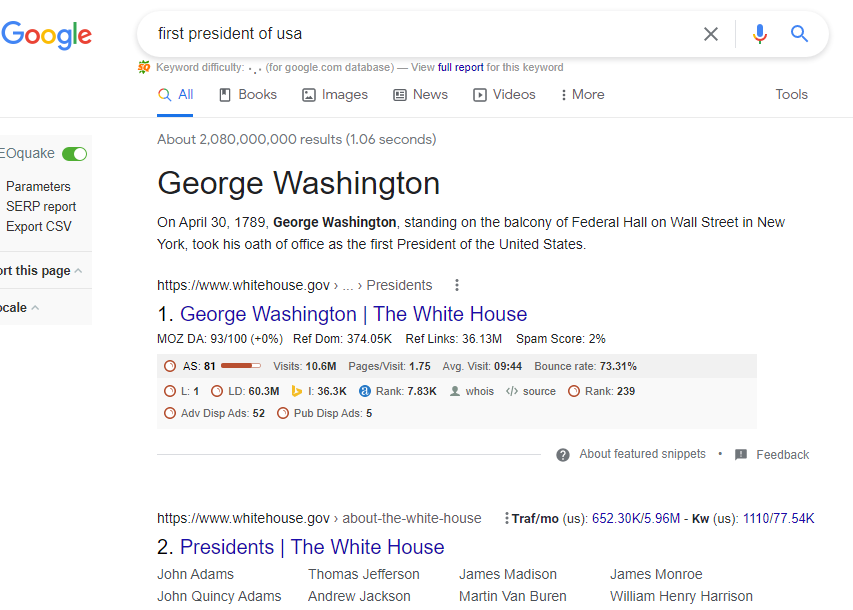
Through information searches, we want Google to answer our questions.
- Brand searches (they aim to reach the brand’s website as quickly as possible. Example = The English cut)
Through brand searches, the user wants to reach the official website of the brand as soon as possible.
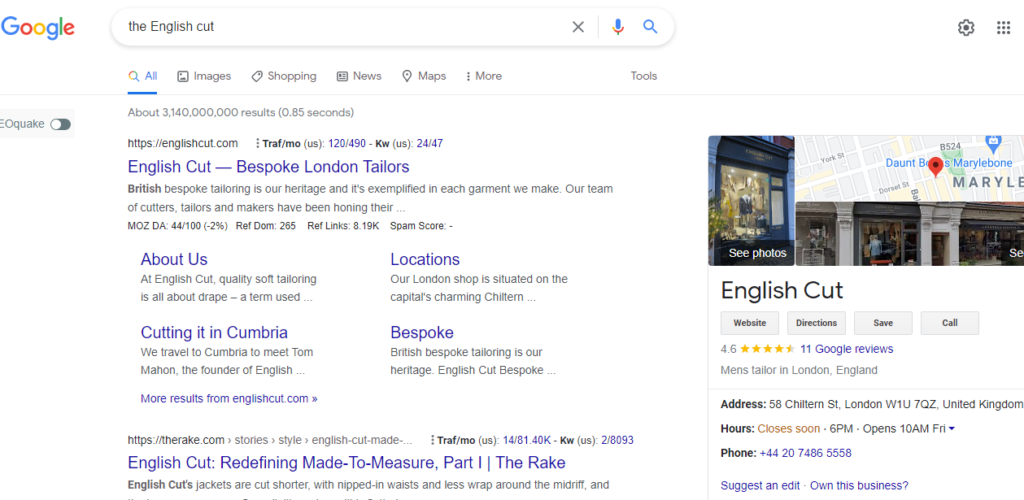
In this case, we see the official website as the first result and an enriched card in the sidebar with the main information of “The English Cut” along with a section of highlighted news.
- Commercial/transactional searches (they are those that provide a greater source of income to businesses since the user is already willing to buy. The user wants to see information about the product, compare it with others, see the experiences of other customers … Example = Asus laptops, best smartphones 2022, best vegan restaurants…).
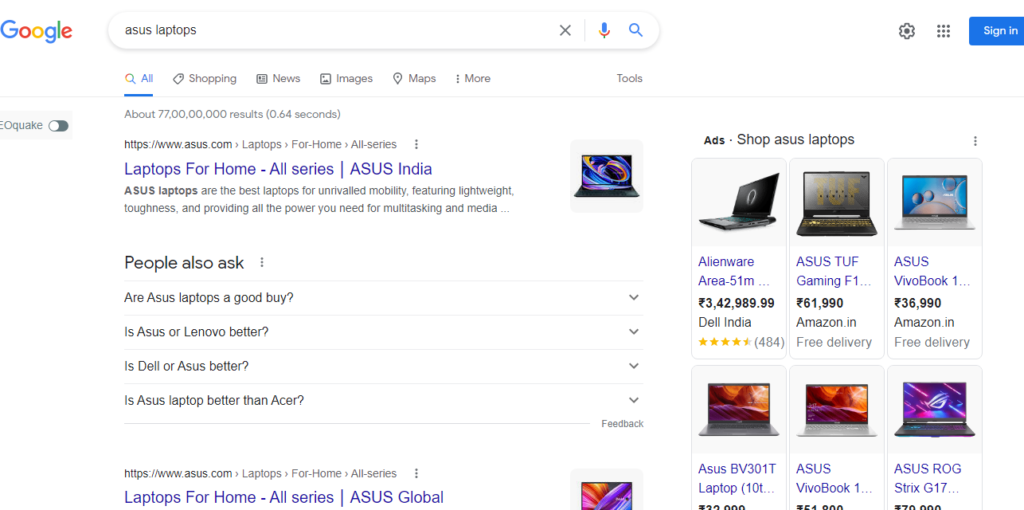
In transactional searches, the user has a greater predisposition to buy, so each click acquires a lot of value. In the image, we see that all the first results are ads (first from Google Shopping and then from Adwords).
TIP: Use a keyword exploration tool or even Google itself and see which pages are in the top positions. So, try to understand why they are there and what content they offer and try to improve it. In particular, pay attention to the type of search and try to offer exactly what the user is looking for. Remember, empathy would be your best weapon.
2. Search Engine Accessibility
If you want your website to appear in Google, allowing you to access it seems logical, right? Something that seems trivial, many times goes unnoticed and we make mistakes such as de-indexing pages that we should not or do not create correct structures. Some points to keep in mind:
- Make sure the robots.txt file is not blocking any important pages
- Make sure no javascript or CSS files are blocking the rendering of the page.
- Confirm that none of the pages that have value for you and your users, are not using the “noindex” tag.
TIP: To check that a page can be read correctly by Google, we can use the “Explore as Google” tool in the Webmaster tools.
Using a browsing tool like Google, you can see how search engines understand each of your pages.
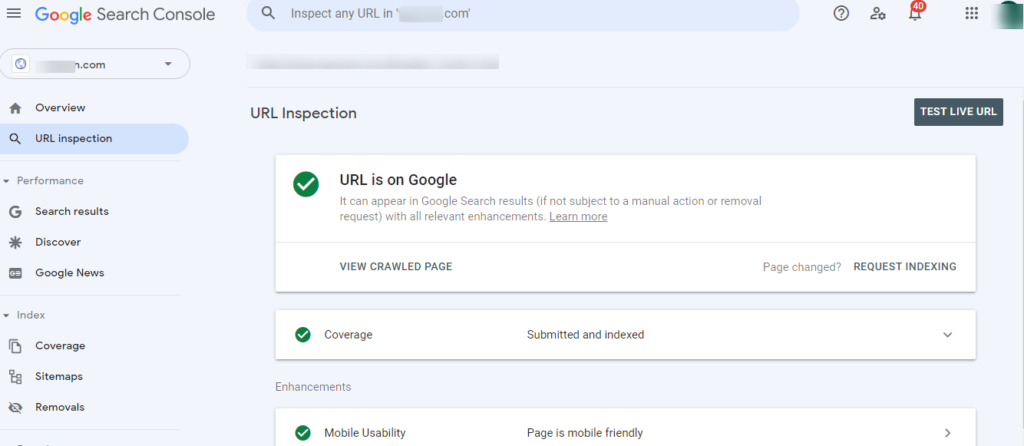
If, on the other hand, we have a website with dozens of web pages (or even thousands) and we want to automate this task, we have very useful tools such as OnCrawl, DeepCrawl, Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, or Content King which will track our website for us and they will help you spot these errors easily.
3. Quality and Quantity of Links
Although it is possible to place pages in the first positions for certain keywords without having any incoming link to our website, having a solid link profile will indeed help us a lot to position our pages.
SEO tools such as Ahrefs.com will be very useful when it comes to performing link analysis.
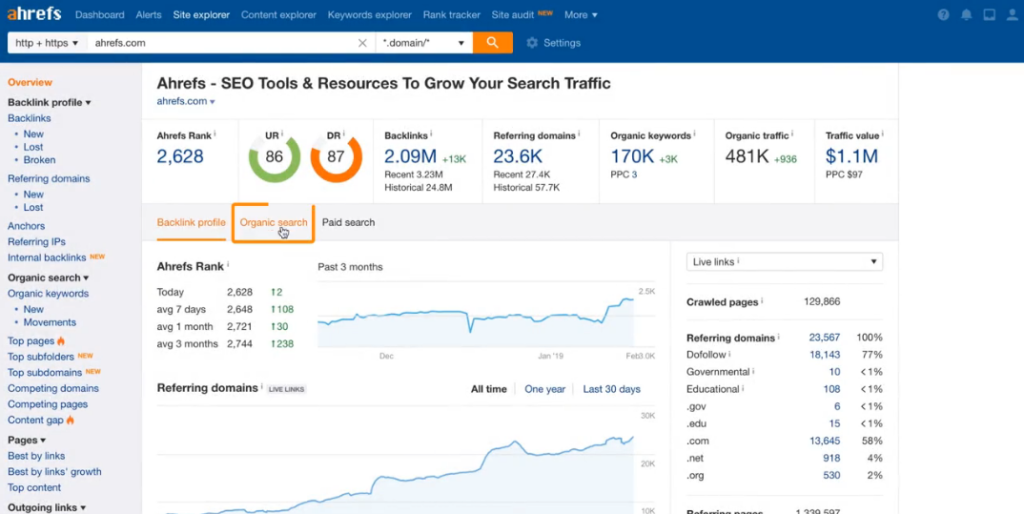
TIP: When creating material, think about creating content that your users want to bookmark, want to share with their friends and they become your brand’s prescribers. If you succeed, you will see how little by little these users from their blogs as companies from their websites, begin to link to you and treat you as a reference. The only thing that you will achieve is to tell Google, “this website is of quality and deserves to be in the top positions.”
4. Unique Content
Without the intention of being repetitive, does it seem obvious right? I don’t have to take other websites and copy their content. Also, you should have your content visible on just one page. It seems simple but it is not as easy as it seems.
Our website must be that apple that stands out among all of them and is unique and incredible.
The general idea is clear. Each page should have:
- Unique title
- Unique description
- Unique content
- A unique url
Duplicate content is surely one of the things that Google has improved the most. Not only are they capable of detecting it and not showing it in their results, but they also know how to distinguish in most cases which url they should show and which ones they should exclude as duplicates.
TIP: To avoid duplicate content, make sure that each page has unique content (title, description, content…) and also that URLs with the same content are not automatically generated. In the world of digital commerce (e-commerce) commonly, we have a page showing, for example, computers and then when applying filters other URLs with parameters are created. These URLs are authentic duplicate content and if we do not act, real ranking massacres can occur.
RECOMMENDED TOOLS: There is a multitude of tools to detect duplicate content. In my case, I would recommend you follow Google’s guidelines to avoid duplicate content and use a tool like Screaming Frog (among others) to analyze duplication.
5. Reputation
EAT ( Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness ), that is, Experience, Authority, and Trust are some of the most relevant concepts used by Google to classify content. It is a concept that can acquire many names but in the end, it represents one thing: reliability. Every time Google recommends a website in the first results (unless it is advertising) it wants to make sure that it is of quality and therefore, the result is excellent and the user is satisfied so that they can access it again to carry out other searches.
In addition, the authority allows sites that a certain route to be differentiated from other recently created sites. One of the elements that have been shown to carry a lot of weight is the age of the domain registration. In other words, as a general rule, companies and domains that have been operating since 2000 will have better positions than recently created domains (provided that the former have followed good practices).
TIP: Authority is not earned in two days. The only “magic potion” to get it is to do things well every day, not be tempted to grow up fast by doing things wrong and we will realize how little by little it grows.
6. Content Updates
At this point, we include 3 fundamental concepts:
- Content “Evergreen”
- Old content update
- Recent content (news)
The content “evergreen” or rephrased as “always green” refers to that content that does not have an expiration date and will always be valid. For example, an article on “how to improve your level of cooking, mechanics or gardening” if this content is well created, will always be valid since regardless of when we read it, it will help us. In addition, it will provide us with a source of recurring traffic over time and a large number of links and authority.
Creating evergreen content is one of the biggest challenges for any professional. Can you imagine creating an article in 2010 and having it continue to receive traffic after 10 years? It’s possible!
On the other hand, we find the update of the old content. The fact that we published an article in 2007 does not mean that we cannot update it again. If we observe that it has a good performance, it is highly recommended to update it, improve its structure and try to convert it into an “evergreen” content.
Finally, when it comes to current content, say that news and videos are gaining in importance as they are being featured very prominently at the top of search results.
TIP: Homework for today! If you have a blog/website, try to identify your best evergreen pages or articles using Google Analytics or some SEO tool and make sure they are up to date, have the correct content, and are taking advantage of their maximum potential.
7. Click rate (CTR)
Every day, Google performs millions of tests through its algorithms to understand which results are the best to show its users. One of them is based on understanding the Click Rate or “Click Through Rate (CTR)”, which is based on measuring how many clicks a page receives compared to the number of views. For example, if 10 people see a result and one click, we would be talking about a CTR of 10%. The higher the CTR, the higher the quality is assumed and therefore the higher the relevance in the search results.
TIP: To get a higher CTR, make sure the content is of quality, optimize the title and the meta-description of the page. This MOZ tool will be very useful to simulate how a page would look in search results.
Although there is no general consensus on the exact length, you can be guided by the following approximate references:
- Title : 50-60 characters or 600px wide
- Meta-description: 140-160 characters
8. Speed and Responsive Web
On March 26, 2018, Google announced that speed would become a fundamental part of its algorithm and that, therefore, it would be a very important factor for positioning.
In this sense, 2 major factors come into play:
- Speed: Ensure that my website is very light in weight, loads quickly and you never make the user wait more than 2 seconds between their request and our response.
- Responsive website: Whether the user visits our website from the computer, from a tablet, or from their smartphones, the experience should be just as pleasant. To achieve this, you can use a responsive design (that the web adapts to each device) or use a separate url: “m.example.com” or “example.com/m”
One of the top priorities for SEO is to make sure that the content can be enjoyed from any device (responsive design).
The responsive design will allow your website users to navigate easily and without problems.
In any case, the maximum objective that we should keep in mind is to offer an excellent user experience and find what they are looking for in a simple and pleasant way.
TOOLS: To make sure you are doing it right, I put at your disposal a set of very useful tools:
- Page Speed Insights: The test will tell us how fast our website is in desktop and mobile version and will buy it with other websites so that you know if they are above or below average.
- Pingdom Tools: This wonderful free tool will allow us to perform speed tests on our website and will also tell us the elements that compose it, the loading time … A marvel!
- Mobile-Friendly Test: Another very useful Google tool that will tell us if our website is ready for mobile devices.
9. Keyword Relevance
In an ideal world, each page would be destined to rank for a family of keywords. In this way, we can ensure that the title, description, and content are focused on this keyword and resolve the user’s intention, and in this way, they can be positioned much better. Trying to make a page rank for very different keywords is dangerous and often does not give good results.
TIP: Try to always rank a page for a keyword family. For example, “football boots.” Within this category, we would find variants such as “football boot”, “football boots”,… but in all cases, we would be talking about the same family of words.
10. Optimized Images
There are many ways to upload images and videos to our website. Still, there are a few ways to get it right. A good SEO strategy for images will be essential.
Each image should:
- Be optimized in size (if it is for a web, there is no need in most cases for it to be larger than 900px wide).
- Be compressed so that the EXIF data is not saved and therefore the images occupy less size.
- Have all an ALT attribute to give context to users and search engines
- Have a friendly name (Shepard-dog.jpg) instead of (4562.jpg)
In addition to selecting those images that we like and impress the most, we must make sure that they are optimized (size, SEO…).
TIP: The most important thing is to make sure that the files are well displayed for users, can be understood correctly by search engines, and occupy as little as possible on our servers.
11. Data Markup, SEO Friendly URLs, and Breadcrumbs
Although Google is a system that is capable of understanding many aspects of your website, the easier you make it, the faster it will crawl your website and better understand your structure, providing you with better positioning. That is why Google recommends data markup (Schema.org), which is, telling Google what type of content you have (a recipe, a video, an article…). Surely, this is one of the things that can make the most difference when it comes to positioning content. Google has fairly complete documentation on this.
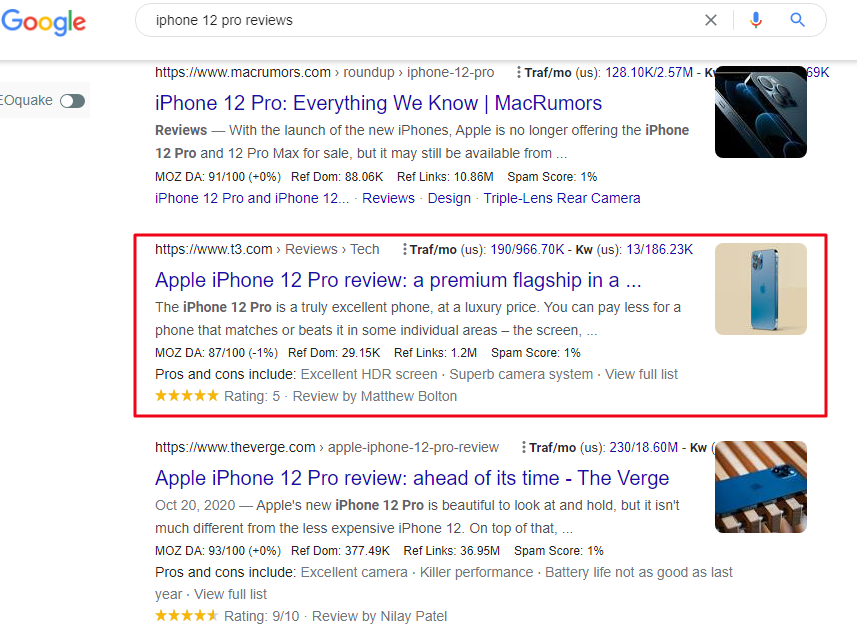
By marking up Schema.org, you can have great visual improvements in search results. In the example, you can see the product reviews.
Another of the key and often forgotten aspects is that of friendly URLs, that is, web address structures that make sense, that are easily readable, and that both for the user and for the search engines, are easy and fast to navigate. . Let’s take an example:
- Example 1: https://example.com/view-fragment157845=caches
- Example 2: https://www.example.com/dogs/shepard
What url do you see best? Is it clear not? In the second, we can see how there is the main domain, a page or category called dogs, and a subfolder called “Shepard”. All pages can be easily found and are grouped in a logical structure.
If you want to go a little further and achieve excellence, it is advisable not only to create correct structures but to tell Google the order of them. To achieve this, you can make a new data markup called ” Breadcrumb or breadcrumbs “, which will tell Google how to categorize the page correctly.
PC Components is an excellent example of good practice. At the top, we can see the implemented breadcrumbs, which facilitate user navigation and search engine crawling.
And this not only applies to the results page but ideally, it should be visible in the visible part of each page:
TIP: Don’t try to create complex structures or make inventions. Create a tree structure in which you see that all the pages on your website can be reached with less than 2-3 clicks. Organize the pages, create categories and you will see that this helps your users a lot, the search engines, and your positioning.
Also, I highly recommend that you read the Google documentation and apply the Schema.org and Breadcrumb markup on your website.
12. Social Impact
We might think that having our corporate profiles on Facebook and Twitter might not be relevant, but it does, and a lot! Google takes into account the impact we have on these networks. In addition, the fact of having social profiles will help us to have a greater reach of our content. In the end it all adds up!
TIP: Define a good Social Marketing strategy and create profiles for your company on these social networks whenever you consider it necessary and useful.
13. Implementation of href = lang
If you have already come this far, it is because you really care about the positioning of your brand and you are taking it seriously. !! Congratulations!!
This part is a bit more technical but not more difficult for that. If we manage a website with only one language, this will not be necessary. On the contrary, if we have our website in several languages or we have different content for areas with the same language (Spanish-Spain vs Spanish-Mexico), then the implementation of hreflang tags is essential.
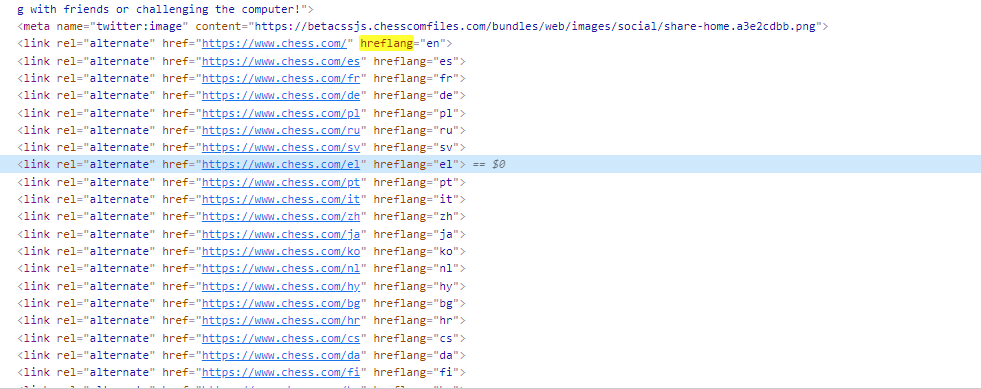
Example of href = lang tags on Chess.com with some of the available languages.
Basically, these are tags that tell Google that a page is also available in other languages and thus prevent it from being considered duplicate content. For example, if you take my case on Chess.com, you’ll see how we have a fairly extensive implementation. By means of the “canonical” tag, we indicate the language of the site being visited, in this case in English, and by means of the “alternate” tags, we indicate that the web is available in all other languages.
TIP: Follow Google’s guide for hreflang implementation and use the Webmaster Tools to verify that the implementation has been correct.
14. Brand Search Volume
Another of the fundamental aspects that Google will take into account is the number of monthly searches that users carry out to search for our brand.
This, for them, is a sign that our site is of quality and that people want to find us to find out or find what they need.
TIP: To know the organic traffic your brand has you can use tools like Ahrefs.com (my recommendation), SemRush, or any other that offers you the approximate monthly volume by keywords.
15. AMP
The AMP technology has become indispensable in the current scenario. In short, this Google technology takes your pages and creates a much lighter version of them, which will be displayed mainly on mobile devices. If you search from your phone, you will see that some results highlighted at the top have a lightning bolt symbol. That’s AMP!
AMP results almost always rank higher on mobile devices.
The vast majority of the news that appears in the carousel are those that have AMP technology implemented.
Although Google has not confirmed it, we can clearly see that AMP pages are almost always better positioned than those that do not have this technology.
TIP: If you use WordPress, download a plugin to implement AMP (super easy to do) and if you have a platform with another CMS or your own code, don’t hesitate to implement it through the official documentation.
16. HTTPS (Secure Browsing)
Safe browsing through a security certificate (HTTPS) is a 100% obligation for any website, be it a small blog or a large company. On February 8, 2018, Google announced that it would mark as “not secure” any website that did not have HTTPS implemented. So that means you have no other choice.
TIP: Many web hosts already have a security certificate implemented in their plan. If not, purchase a certificate from a trusted company.
17. Parameter Control and robots.txt
Closely related to the duplicate content section, we find the robots.txt file and the management of parameters in the Google Webmasters tools. In both cases, the main idea is to prevent the filters and other characteristics of our website from creating tens or even thousands of pages with the same content or sometimes with empty content.
TIP: Regarding the control of parameters, make sure that all the URLs that include filters, be they price, city, or any other characteristic, are not being indexed and have a “canonical” towards the main page.
Regarding the robots.txt file, the first thing is to make sure that it is not blocking any important page and once you have this confirmed, you can add all those pages that should not be known by Google, such as your administration panel and other sensitive pages. In this way, we will prevent Google from trying to see pages that it shouldn’t.
Creating a robots.txt file is very simple. You just have to add the following in a .txt file
- User-agent: Googlebot
- Disallow: / PAGE YOU DON’T WANT TO TRACK /
You can add as many disallow as you want, as long as they make sense.
18. Sitemaps
If we added pages to the robots.txt file to prevent Google from crawling them, the opposite is true for sitemaps. They are files that you upload to your server to tell Google all the pages you have and thus make it easier to track them.
You can have several types of sitemaps:
- For images
- For videos
- For news
- Generic with pages and articles
TIP: Read the Google documentation about it and create sitemaps of your website so that Google can track it more easily.
19. Passion!
Until now, all the points had been more or less technical, but you can never forget about this ingredient. Without passion, perseverance, and hard work, there are no results. A good web positioning strategy requires many hours, sacrifice, and above all the desire to learn and improve every day. If you do your part, sooner or later the results will not take long to appear. To enjoy!
Illusion, perseverance, and effort are the only secret ingredients to succeed in our SEO strategy.
I sincerely hope that you have enjoyed this short guide as an introduction to the world of SEO and I would love to see your comments (questions, suggestions, ideas…).
If you have an interesting project and you want help to improve your positioning, do not hesitate to contact me.

Hi, this is a comment.
To get started with moderating, editing, and deleting comments, please visit the Comments screen in the dashboard.
Commenter avatars come from Gravatar.